Apheresis
Apheresis refers to the process of separating the cellular and soluble components of blood using a machine. Apheresis is often done on donors where whole blood is centrifuged to obtain individual blood components (eg, red blood cells [RBCs], platelets, plasma based on specific gravity) to use for transfusion in different patients. Apheresis may also be used therapeutically to treat various disorders.
Easy Medical Visa Approvals
Travel Booking Assistance
Comprehensive Treatment Plans
Multi-Language Support
Apheresis refers to the process of separating the cellular and soluble components of blood using a machine. Apheresis is often done on donors where whole blood is centrifuged to obtain individual blood components (eg, red blood cells [RBCs], platelets, plasma based on specific gravity) to use for transfusion in different patients. Apheresis may also be used therapeutically to treat various disorders.
Symptoms Of Apheresis
Symptoms
Types of conditions
There are five main types of Apheresis
Administration of high-dose corticosteroids
Prescription of statin medication
Blood transfusion
Administration of anticonvulsant medication
Initiation of immunosuppressive therapy
Administration of high-dose corticosteroids
Corticosteroids help suppress the immune response to prevent rejection of the transplanted organ.
Types of Conditions Treated by Apheresis
Here are several conditions and their associated symptoms that can be managed or alleviated through apheresis:
Autoimmune Disorders: In autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis, myasthenia gravis, or Guillain-Barré syndrome, apheresis can help remove harmful antibodies from the blood that are attacking the body's own tissues. Symptoms of autoimmune disorders vary widely but may include weakness, fatigue, numbness, tingling, and difficulty with movement or coordination.
Neurological Disorders: Certain neurological conditions, such as chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) or some types of neuropathies, can lead to symptoms like muscle weakness, sensory disturbances, and pain. Apheresis may be used to remove factors contributing to nerve damage or inflammation.
Haematological Disorders: Apheresis is also utilised in the management of various haematological disorders, including thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) and certain types of hemolytic anemias. These conditions can cause symptoms such as excessive bruising and bleeding, fatigue, and shortness of breath due to decreased oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood.
Hyperlipidemia: In cases of severe hyperlipidemia or familial hypercholesterolemia where diet and medication alone aren't sufficient, apheresis can be employed to reduce levels of LDL cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood, potentially reducing the risk of cardiovascular events. Symptoms of hyperlipidemia typically include chest pain, leg pain, and other symptoms of cardiovascular disease.
Organ Transplant Rejection: Apheresis can be used to remove antibodies that may cause rejection of transplanted organs, such as kidneys or lungs. Symptoms of organ rejection vary depending on the organ affected but may include fever, decreased organ function, and pain or tenderness over the transplant site.
Diagnosis
Apheresis, a specialised medical procedure, is pivotal in diagnosing and managing various disorders by selectively removing specific blood components. It aids in diagnosing autoimmune diseases such as myasthenia gravis and Guillain-Barré syndrome, haematological disorders like thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) and hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS), and neurological conditions including multiple sclerosis and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP). Furthermore, apheresis facilitates the diagnosis and treatment of renal disorders such as focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) and Goodpasture syndrome, certain blood disorders like leukaemia and sickle cell disease, and metabolic disorders such as familial hypercholesterolemia and porphyria.
Risk Factors
- Allergic reactions- Some people may be allergic to plasma or red blood cells that providers use to replace blood cells during apheresis.
- Bleeding- Sometimes, the process of inserting a needle into a blood vessel to obtain blood causes excessive bleeding.
- Blood clots- People with underlying conditions like cancer, diabetes or cardiovascular disease are at risk for blood clots.
- Electrolyte imbalance- Electrolytes are minerals in your body that support important body functions. Your electrolyte levels may go up or down during apheresis.
- Fluid overload- Rarely, too much fluid returns to your body during apheresis, causing swelling.
- Nerve damage- Occasionally, inserting a needle or catheter damages nerves and causes numbness, tingling or weakness.
Preparing For Surgery
- Medical Evaluation: Your healthcare provider will conduct a thorough assessment of your health status, review your medical history, and perform any necessary tests to ensure you're fit for the apheresis procedure.
- Discussion of Procedure: Your doctor will explain the apheresis procedure, its purpose, potential risks, and expected outcomes. Take this opportunity to ask any questions you may have and ensure you fully understand what to expect.
- Medication Adjustment: Inform your doctor about any medications you're currently taking, including prescription drugs, over-the-counter medications, and supplements. Some medications, especially blood thinners, may need to be adjusted or temporarily stopped before the procedure to minimize the risk of bleeding.
- Fasting: You may be instructed to refrain from eating or drinking anything for a certain period before the apheresis procedure. This is typically done to ensure your stomach is empty, reducing the risk of complications during the procedure.
- Hydration: It's essential to stay well-hydrated before the apheresis procedure. Follow any specific instructions provided by your healthcare provider regarding fluid intake leading up to the surgery.
- Arrange Transportation: Since you may receive sedation during the apheresis procedure, arrange for someone to drive you home afterward. Avoid driving or operating machinery for the remainder of the day due to potential side effects of sedation.
- Follow Preoperative Instructions: Your healthcare provider will provide specific instructions on how to prepare for the apheresis procedure. This may include guidelines on bathing, skincare, and clothing to wear on the day of the surgery.
- Mental Preparation: Surgery can be stressful, so take time to relax and mentally prepare yourself. Engage in activities that help reduce stress and anxiety, such as deep breathing exercises or meditation.
- Follow-up Care: Understand the postoperative care plan, including any restrictions on activities and medications. Follow your doctor's instructions carefully for optimal recovery and follow-up appointments.
Treatment Details
In general, this procedure follows the steps:
- You’ll sit in a comfortable chair or on a bed.
- Your provider will insert a needle into a vein in each of your arms. Each needle connects to a catheter, which is a thin, flexible tube. In some cases, your provider may use a central venous catheter.
- One catheter carries blood from your body to the machine that will separate blood elements.
- Once that’s done, the catheter in your other arm returns the remaining blood elements to your body.
Types
- Plasma Exchange: Plasma exchange involves removing a portion of the patient's plasma, the liquid component of blood containing antibodies and other proteins, and replacing it with replacement fluid or donor plasma.
- Red Blood Cell Exchange (Erythrocytapheresis): Red blood cell exchange specifically targets the removal of red blood cells from the patient's bloodstream while preserving other blood components. 3.Plateletpheresis: Plateletpheresis is focused on isolating and collecting platelets from the patient's blood while returning the remaining blood components back to the circulation.
- Leukapheresis: Leukapheresis involves the selective removal of white blood cells (leukocytes) from the patient's bloodstream, aiming to reduce their concentration to therapeutic levels.
- Lipid Apheresis: Lipid apheresis targets the removal of lipids, particularly cholesterol and triglycerides, from the patient's blood, effectively lowering lipid levels and reducing the risk of cardiovascular complications.
Technology Used
- Centrifugation: Uses rotation to separate blood components by density.
- Membrane Filtration: Selectively filters blood components based on size.
- Adsorption: Utilises adsorbent materials to remove specific substances from blood.
- Continuous Flow Apheresis: Allows continuous blood processing without interruption.
- Photopheresis: Treats immune disorders by exposing blood to ultraviolet light.
- Cell Separation: Isolates specific blood cell populations for therapeutic or analysis purposes.
Recovery
- Rest: Allow yourself sufficient time to rest and recuperate following the apheresis procedure to aid in recovery.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of fluids to help replenish lost fluids and maintain hydration levels after the procedure.
- Monitoring: Follow-up appointments may be necessary to monitor your progress and ensure optimal recovery.
- Activity Restrictions: Depending on the type of apheresis performed, your healthcare provider may recommend certain activity restrictions for a specified period to prevent complications.
- Symptom Management: Report any unusual symptoms or discomfort to your healthcare provider promptly for appropriate management and intervention.
- Follow-up Care: Adhere to any post-procedure care instructions provided by your healthcare provider, including medication regimen and dietary recommendations, to support your recovery process effectively.
Your journey to good health begins here

Accredited Hospitals
Nationally accredited hospitals for high-quality care

Multi-language Support
Convey your needs in the language you're most comfortable in

Travel Booking Assistance
Seamless booking assistance for your healthcare journey

Personalised Treatment Plans
A treatment journey tailored to all your preferences and needs

Unparalleled Hospitality
Experience exceptional hospitality during your stay

Easy Medical Visa Approvals
Dedicated assistance for medical visa requirements
Plan your healthcare journey with Karetrip!
India’s Best Hospitals are Partnered With Karetrip
Access World-Class facilities from top Hospitals across India
Consult with India’s most experienced doctors
Experience premium care from India’s leading specialists

Dr. V V Lakshminarayanan
Nephorologist
45+ Years Of Experience

Dr. Ashok Kumar R
Nephrologist
21+ Years Of Experience

Dr. Sathish M. Rao
Nephrologist
33+ Years Of Experience

Dr. Navdeep Singh Khaira
Nephrologist
38+ Years Of Experience

Dr. Sandeep Guleria
Nephrologist
35+ Years Of Experience

Dr. Alka Bhasin
Nephrologist
24+ Years Of Experience
Cost Estimation
Learn about the expenses involved in the procedure and what factors affect them.
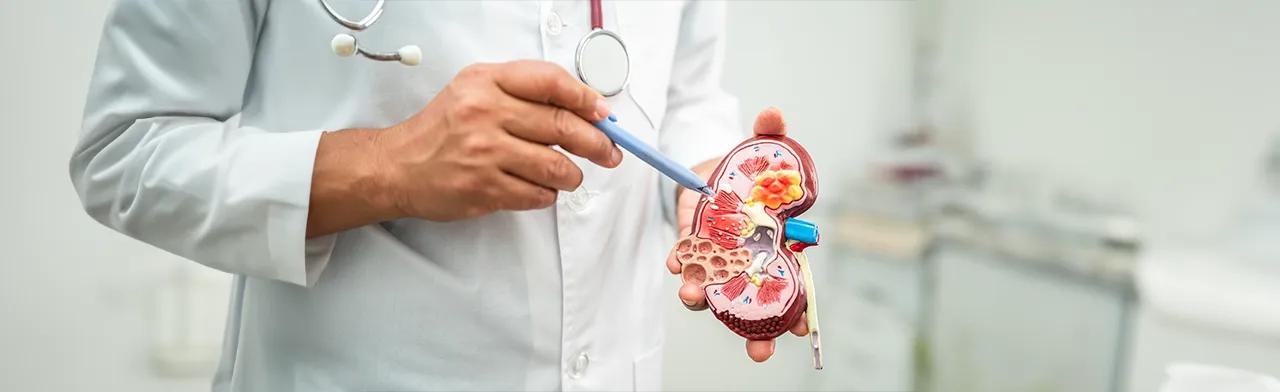
The cost of Apheresis varies due to several factors. Hospital charges, Pre-operative tests, and type of Apheresis all contribute to the total expense. Location also impacts expenses. Insurance coverage affects individual costs, including deductibles and copayments. Our team can help you understand the precise costs based on your specific case and doctor’s recommendations.
The average cost of the Apheresis in India is around ₹ 10,000 to ₹ 25,000.
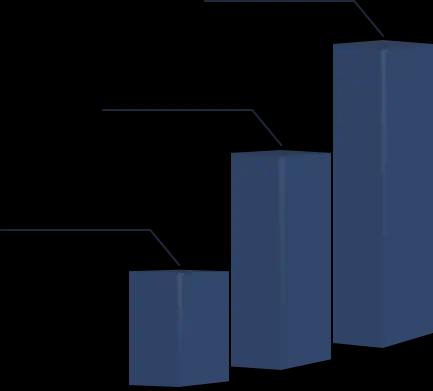
₹ 25,000
High Cost
₹ 15,000
Average Cost
₹ 10,000
Low Cost
The LIST of AVERAGE COST of the Apheresis across TOP 6 cities in India in Indian Rupee (INR) is as follows :
City
Lowest Cost
Average Cost
Highest Cost
Delhi/NCR
₹ 15,000
₹ 20,000
₹ 25,000
Tamil Nadu
₹ 10,000
₹ 15,000
₹ 18,000
Karnataka
₹ 12,000
₹ 18,000
₹ 22,000
Telangana
₹ 14,000
₹ 19,000
₹ 24,000
West Bengal
₹ 11,000
₹ 15,000
₹ 19,000
Gujarat
₹ 13,000
₹ 19,000
₹ 21,000
Commonly Asked Questions
What is apheresis?
Apheresis is a medical procedure where blood is withdrawn from a donor or patient, specific components are separated using a machine, and the remaining blood is returned to the donor or patient.
How does apheresis work?
During apheresis, blood is drawn from the individual into a machine called an apheresis machine. Inside the machine, the blood is separated into its components, such as red blood cells, plasma, platelets, or white blood cells, depending on the purpose of the procedure. The desired component is retained, while the rest of the blood is returned to the individual.
What are the different types of apheresis?
Apheresis can involve the removal of specific blood components, including:
- Plateletpheresis: Removal of platelets from the blood.
- Plasmapheresis: Removal of plasma from the blood.
- Red cell exchange: Removal of abnormal red blood cells and replacing them with healthy donor red blood cells.
- Leukapheresis: Removal of white blood cells from the blood.
What is apheresis used for?
Apheresis is used for various medical purposes, including:
- Treating certain autoimmune diseases by removing harmful antibodies from the blood.
- Collecting specific blood components for transfusion, such as platelets or plasma.
- Managing conditions like sickle cell disease or leukemia by removing abnormal blood cells.
- Harvesting stem cells for transplantation.
Is apheresis safe?
Generally, apheresis is considered safe when performed by trained medical professionals in a clinical setting. However, like any medical procedure, it may carry some risks, such as bleeding, infection, or reactions to anticoagulants used during the process.

Do you still have a query?


"I had a successful surgery at Fortis Escorts Hospital, and it was all thanks to Karetrip's help in finding the right hospital for me. The entire process was smooth and stress-free, with Karetrip handling all the arrangements and answering any questions I had. The medical team at the hospital was outstanding, and the facilities were top-notch. I highly recommend Karetrip to anyone looking for a tension-free healthcare experience."
Read MoreFatima
Chattogram


"Thanks to Karetrip, I got connected with MAX Hospital in New Delhi. The team guided me through every step – from finding the right doctor to handling travel and visas. They made a daunting process feel like a breeze. The care I received at MAX Hospital was outstanding, and I can't thank Karetrip enough for making it possible. They truly put patients first and go the extra mile to ensure a smooth healthcare journey. I'm grateful beyond words!"
Read MoreHasan
Dhaka


"At first, I was unsure about having a medical procedure done in a foreign country. However, Karetrip's team at Indraprastha Apollo Hospital made me feel much better. The hospital was very clean, modern, and had everything they needed to help me. The staff were very kind and did everything they could to make me feel comfortable. I'm really happy with how my treatment turned out, and I appreciate Karetrip for making it easy and stress-free."
Read MoreImran
Sylhet
 Google Reviews4.9/5
Google Reviews4.9/5




I had a successful surgery at Fortis Escorts Hospital, and it was all thanks to Karetrip's help in finding the right hospital for me. The entire process was smooth and stress-free, with Karetrip handling all the arrangements and answering any questions I had. The medical team at the hospital was outstanding, and the facilities were top-notch. I highly recommend Karetrip to anyone looking for a tension-free healthcare experience.
Fatima
Chattogram
 Google Reviews4.9/5
Google Reviews4.9/5